California’s Electricity Grid, Explained
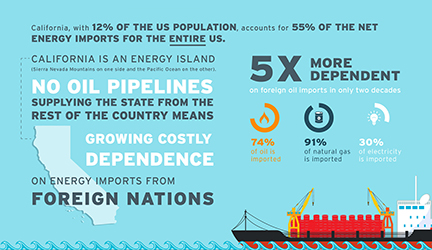
Every minute of every day, people flip a switch and in an instant, a light comes on. Power, on call and at our finger tips anytime day or night, is so expected and so taken for granted that most of us don’t even give it a thought. But where does that power come from? California’s power supply in 2017 was about 34% natural gas, 29% renewable, 15% large hydro, 9% nuclear, 4% coal and 9% other unspecified sources.
In Los Angeles, much of the city’s electricity comes from three natural gas-fired power plants – Scattergood, Haynes and Harbor. Los Angeles Mayor Eric Garcetti’s announcement on February 12th that the Department of Water and Power (DWP) will stop retrofitting these three power plants and will instead shut them down. The important question remains how will the facilities be replaced without raising energy prices or creating power outages? And, how will DWP meet increasing demand as it shuts down reliable generation? The main challenge is that the two most talked about sources of renewable energy, solar and wind power, are intermittent, generating electricity only when the sun shines or the wind blows. Plus, Los Angeles County has banned utility scale wind turbines in unincorporated areas, so Los Angeles has also taken local wind generation off the table.
In a Los Angeles Times article published the same day, Kendal Asuncion, a public policy manager for the Los Angeles Area Chamber of Commerce, said the city’s environmental goals must be “balanced with resiliency, responsibility and financial responsibility” to keep power flowing smoothly and electricity rates affordable. “Businesses are concerned about these impacts to our bottom line, and we’re concerned that there was no ratepayer advocate report or analysis done on this,” Asuncion said at Tuesday’s board meeting.
Californians already pay some of the highest electricity rates in the nation, and even before the Mayor’s decision, DWP had previously announced a 21% increase in electricity rates through 2021 to meet state renewable mandates. As lawmakers, engineers, planners and operators race to redesign California’s complex electricity grid to adapt to the state’s aspirational environmental goals, let’s take a look at how power gets to the homes and businesses of every Californian. For most of us, the power journey starts long before we flip the switch.
VIDEO: “CALmatters Explains The Power Grid”
Produced by Julie Cart, Environmental Reporter at CALmatters